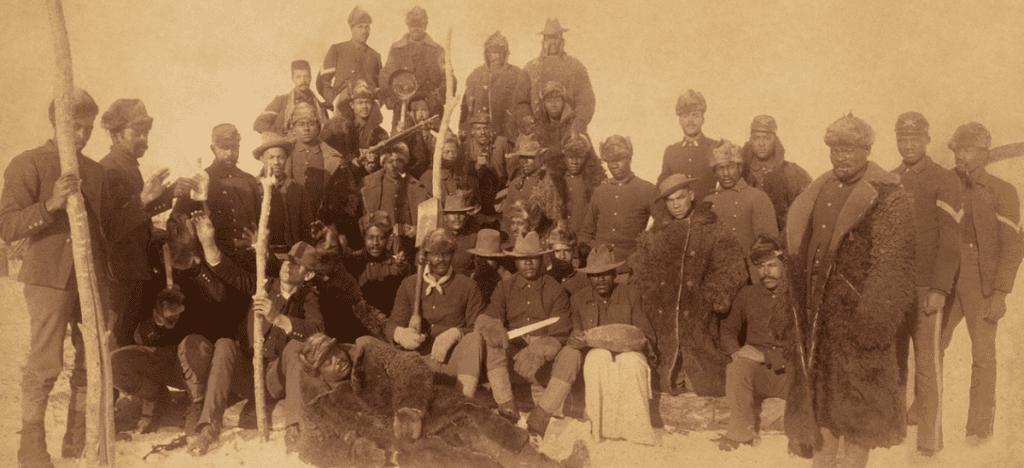
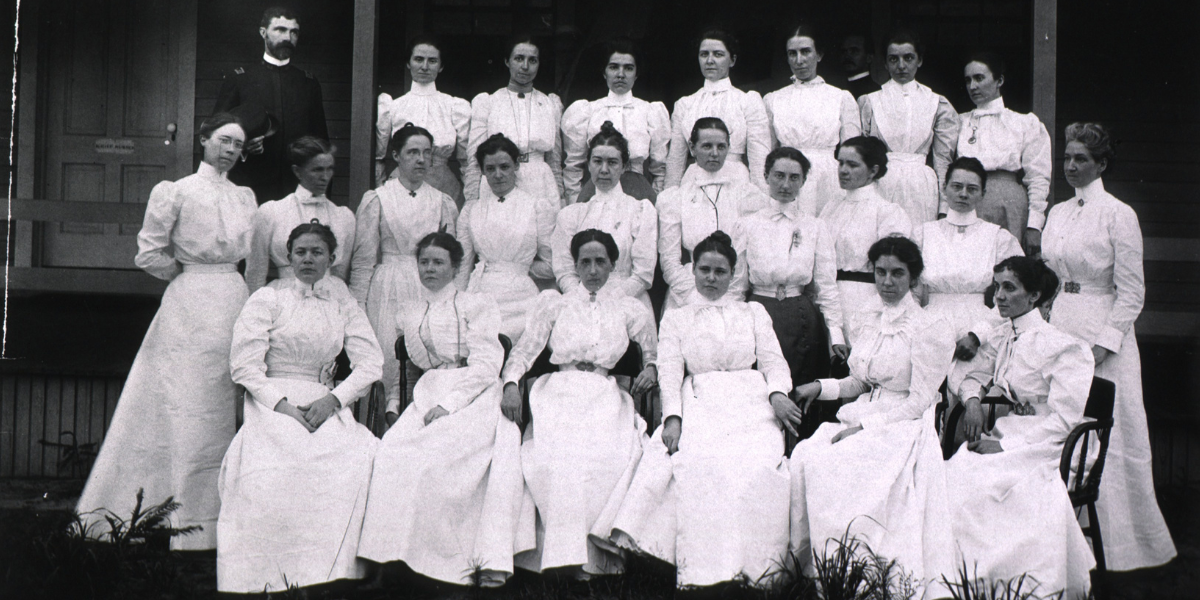
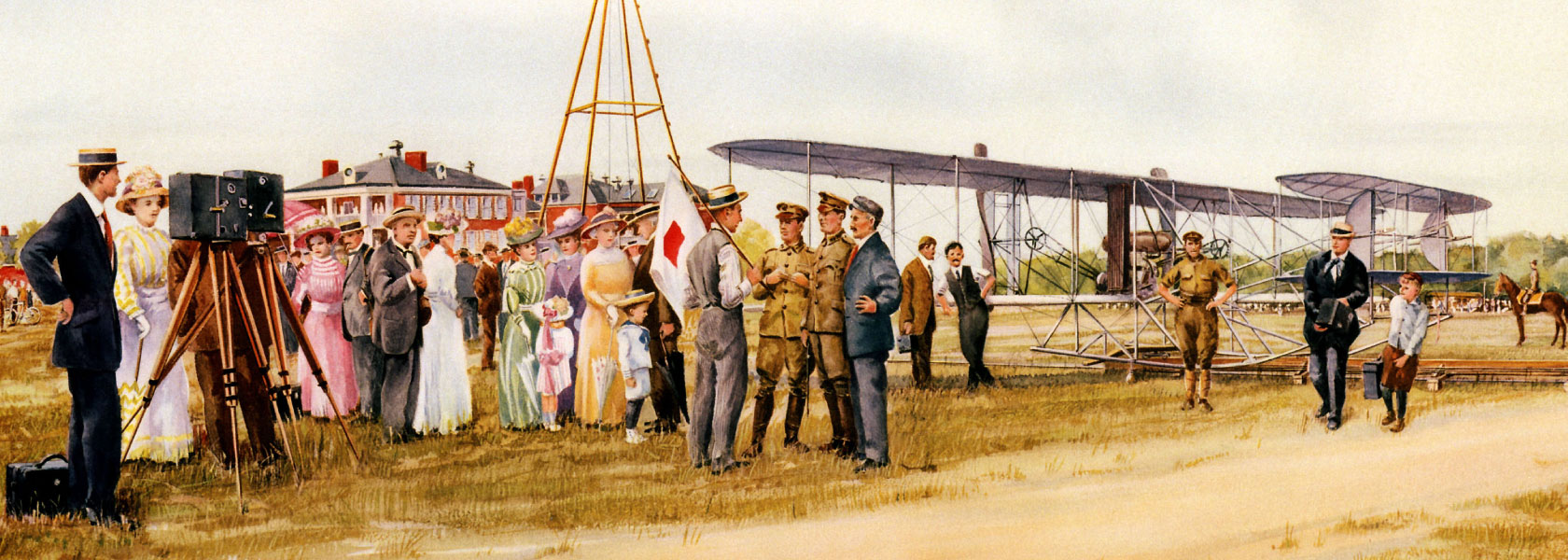
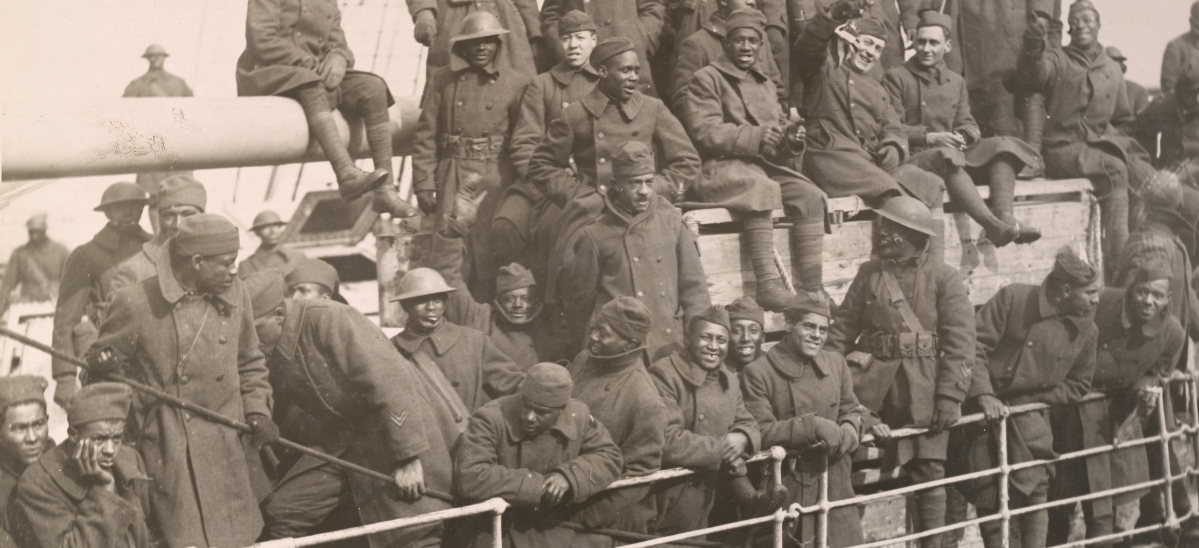
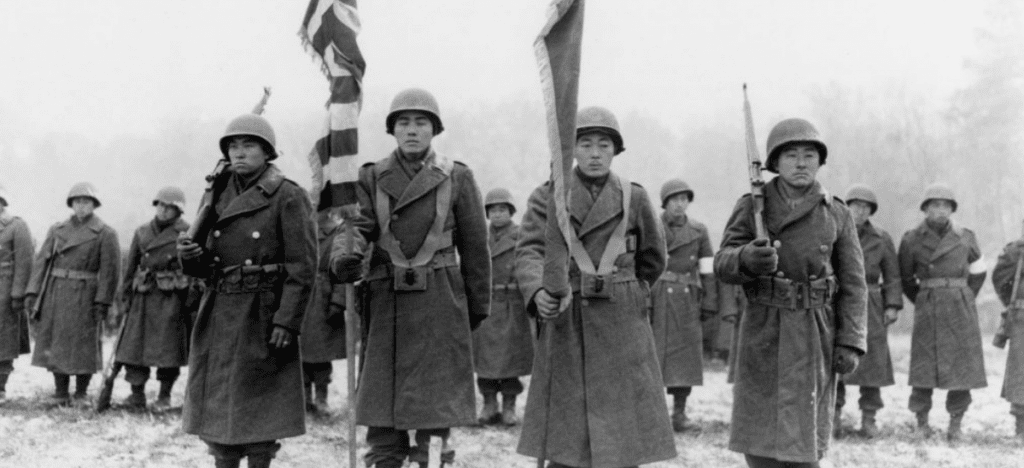
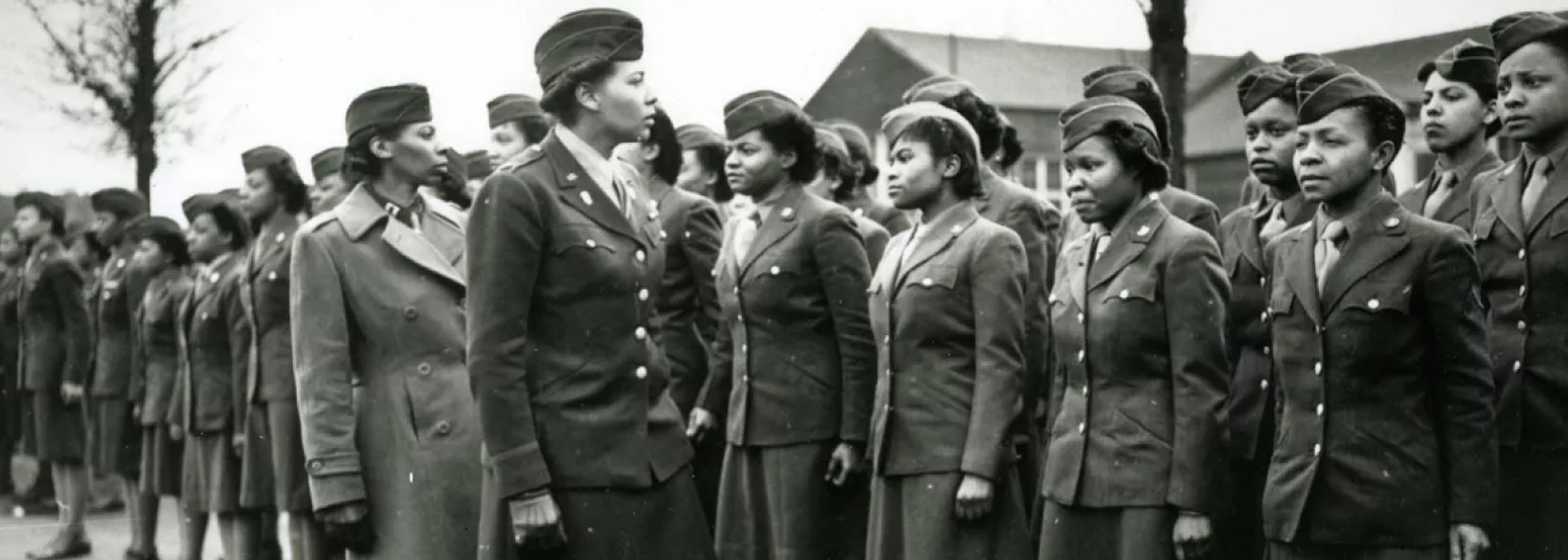
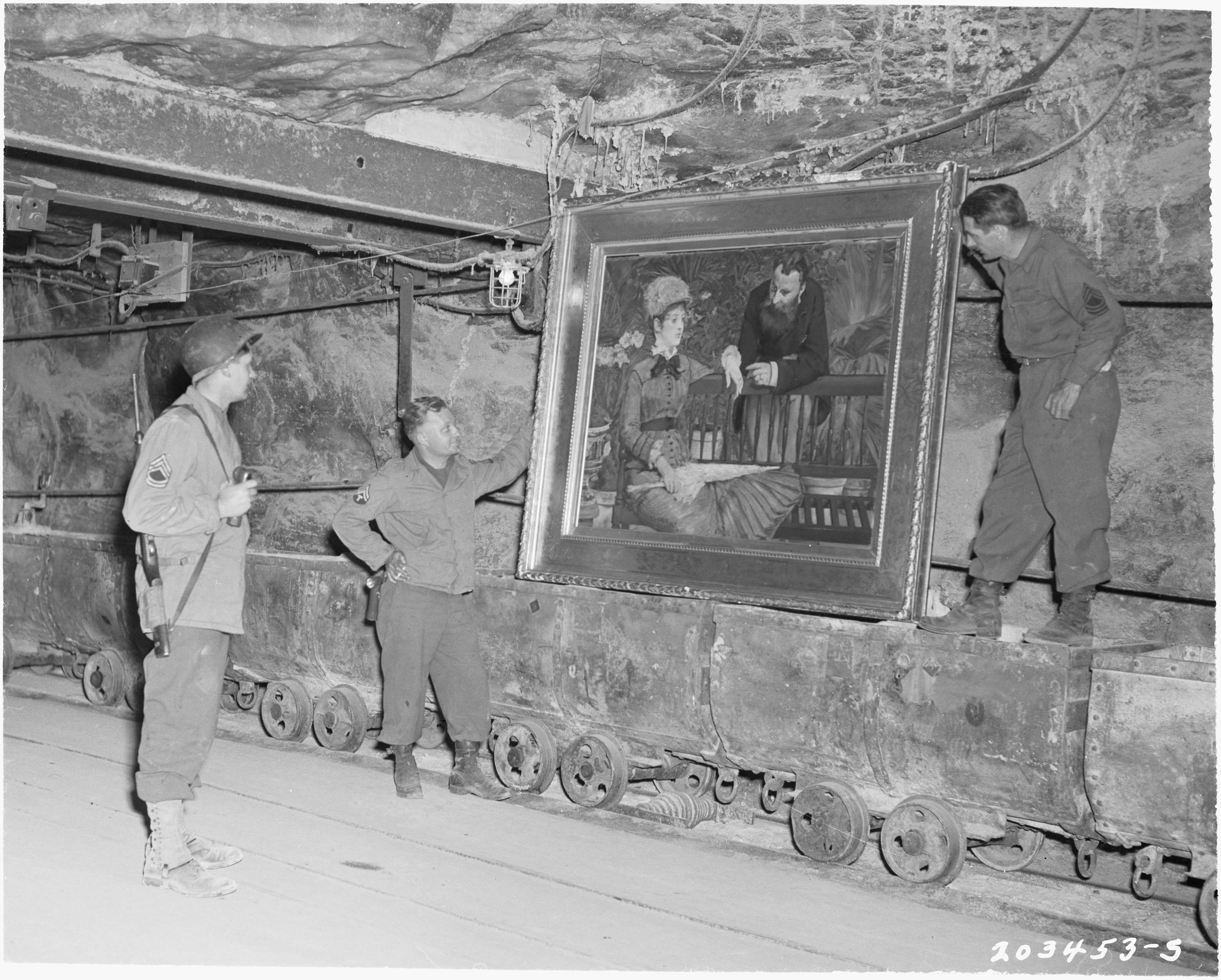
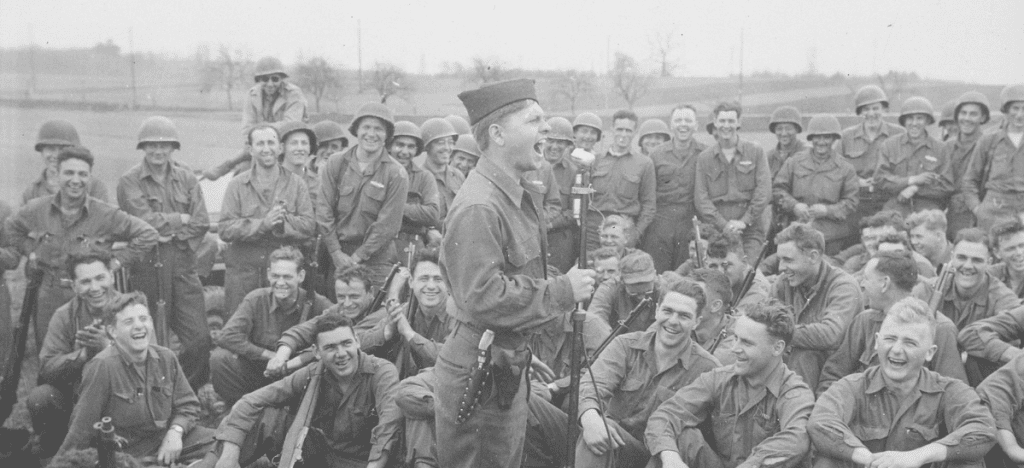
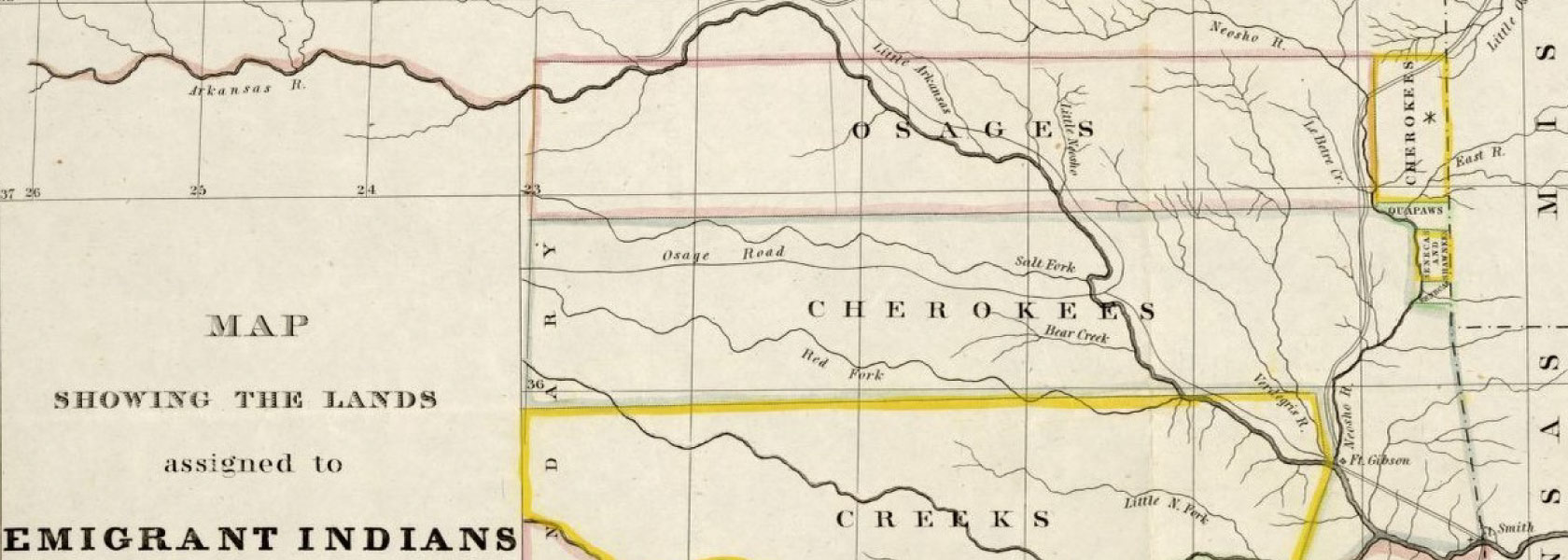
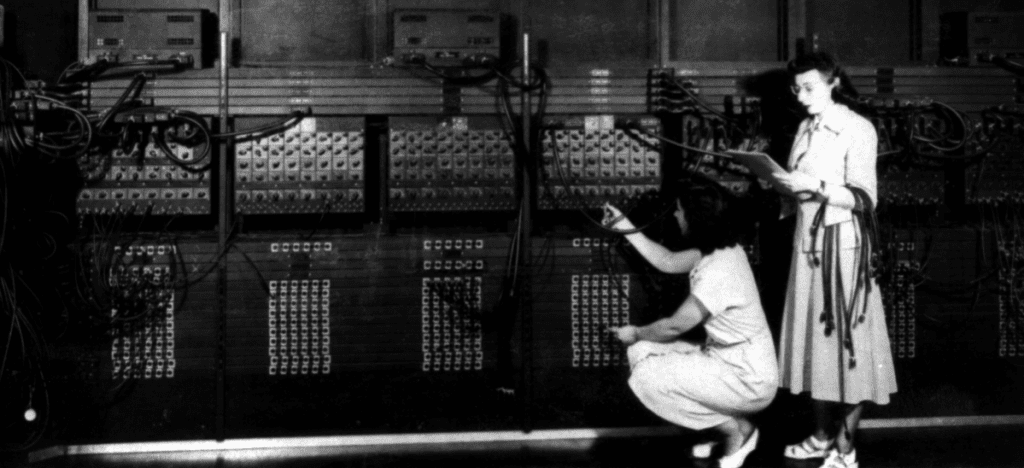
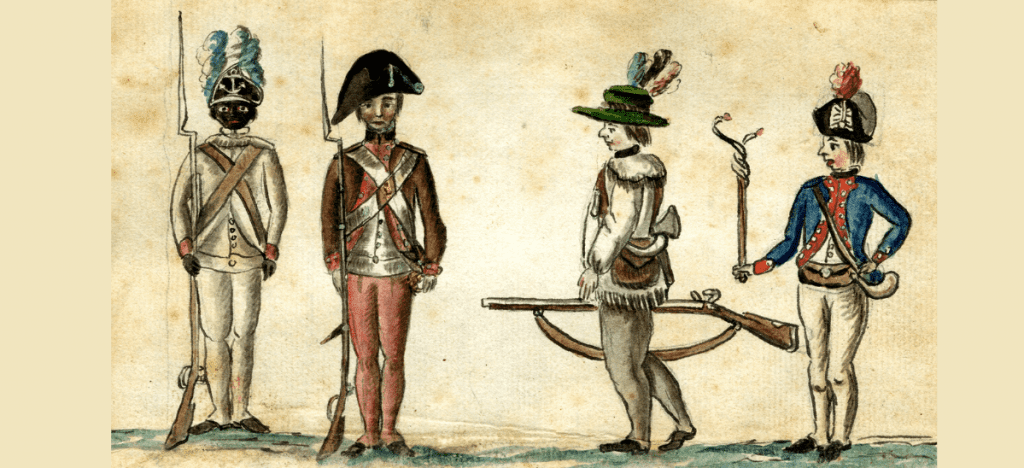Army Trails
Explore Our Army TrailsNews and Articles
View Our News & Articles- visit
- exhibits
- army trails
- public programs
- education
- events
- news
- about
- get involved
Back
Visit the Museum
Plan Your Visit
Back
Back
Public Programs
Army 250
Back
Programs & Education
Learning Opportunities
Back
Events
Opening Weekend June 7-8
Back